IKARI curve
IKARI curve
Ikari L both for left and right coronary arteries
IKARI curve
ST elevation acute myocardial infarction (STEMI)
Primary PCI from radial access reduces mortality in patients with STEMI.
Reduction of reperfusion time achieves better mortality in radial access.
If Ikari L is applied to both left and right coronary artery, it can reduce reperfusion time.
Steps of Primary PCI
<Conventional method>
1) Radial artery puncture
2) Insertion of diagnostic catheter (L)
3) Engagement of diagnostic catheter (L) for LCA
4) Angiography of LCA
5) Removal of the catheter (L)
6) Insertion of diagnostic catheter (R)
7) Engagmennt of diagnostic catheter (R) for RCA
8) Angiography of RCA
Removal of the catheter (R)
10) Insertion of a guiding catheter
11) Engagement of the guiding catheter
12) Guidewire passage
13) First device activation (balloon or thrombus aspiration)
=Reperfusion
<Ikari L both for left and right>
1) Radial artery puncture
2) Insertion of Ikari L
3) Engagement of Ikari L for LCA
4) Angiography of LCA
7) Engagmennt of Ikari L for RCA
8) Angiography of RCA
12) Guidewire passage
13) First device activation (balloon or thrombus aspiration)
=Reperfusion
If Ikari L is used both for left and right coronary arteries, it can reduces a total of 5 steps; insertion of catheters from 3 to 1, removal of catheter from 2 to 0, and insertion of catheter from 3 to 2. Thus, it can reduce reperfusion time naturally.
Puncture to balloon time in Tokai University
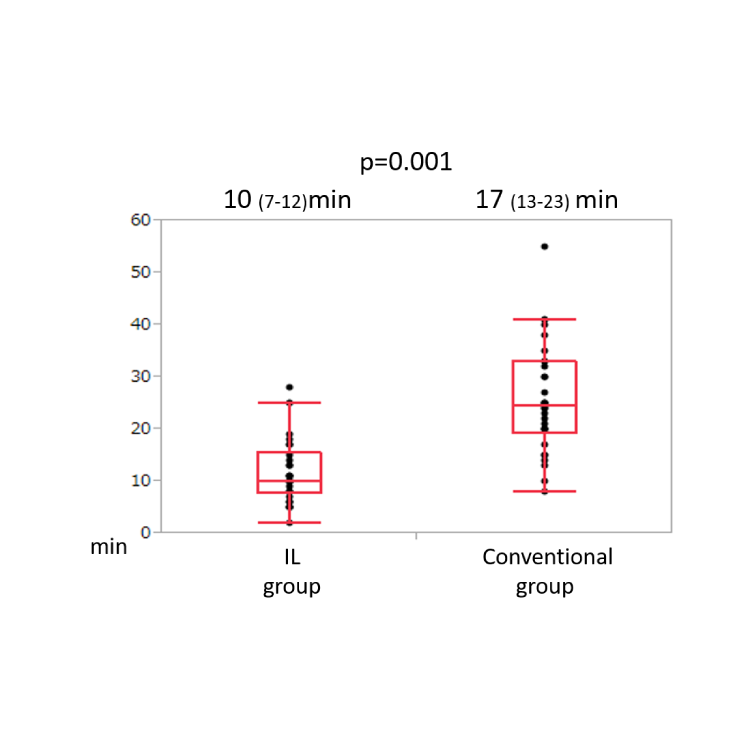 Significan reduction of reperfusion time was achieved.
Significan reduction of reperfusion time was achieved.
Cardiovasc Interv and Ther DOI 10.1007/s12928-016-0395-z

